The Unseen Guardians of Electricity: Transformer Monitoring and Diagnostics
Electricity, our modern lifeblood, flows through a vast network of invisible conductors and regulators that we scarcely think about — until something goes wrong. Step-down transformers, the unsung heroes of electrical distribution, play a crucial role in our daily power supply. Yet, their reliability is often taken for granted.

For electrical engineers and facility managers, the realm of monitoring and diagnostics surrounding step-down transformers is as integral to the system’s health as protective measures in human healthcare. This narrative traverses the world of transformers, outlining not just their function but also how vigilance through monitoring and diagnostics can prevent catastrophic electrical failures.
Understanding Step-Down Transformers
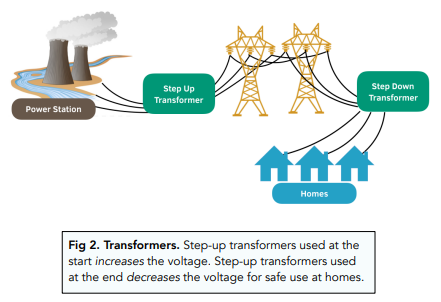
Step-down transformers are the backbone of electrical power systems. Their primary role is in reducing the high voltages received from power generation or transmission systems to levels suitable for industrial and domestic usage. They ensure that the electricity reaching our homes and businesses is at a safe and practical voltage level.
Role in Electrical Distribution
At substations or industrial complexes, these transformers serve to reduce voltage levels from typically 69 kV to levels as low as 120 volts for safe consumer use. They also provide circuit isolation, which protects sensitive equipment from overload and safeguards against earth faults.
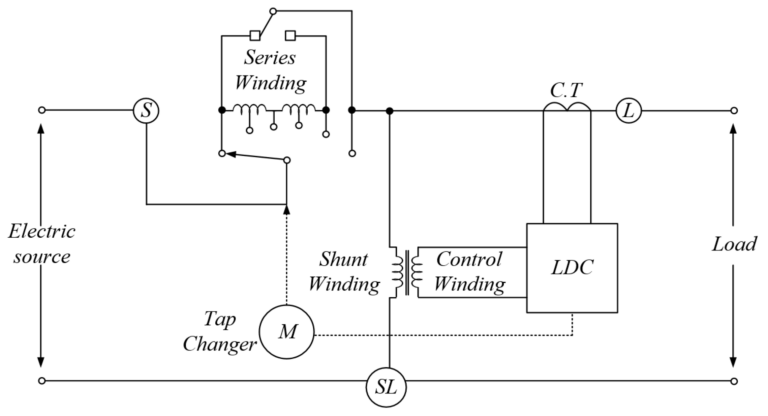
Key Components Explained
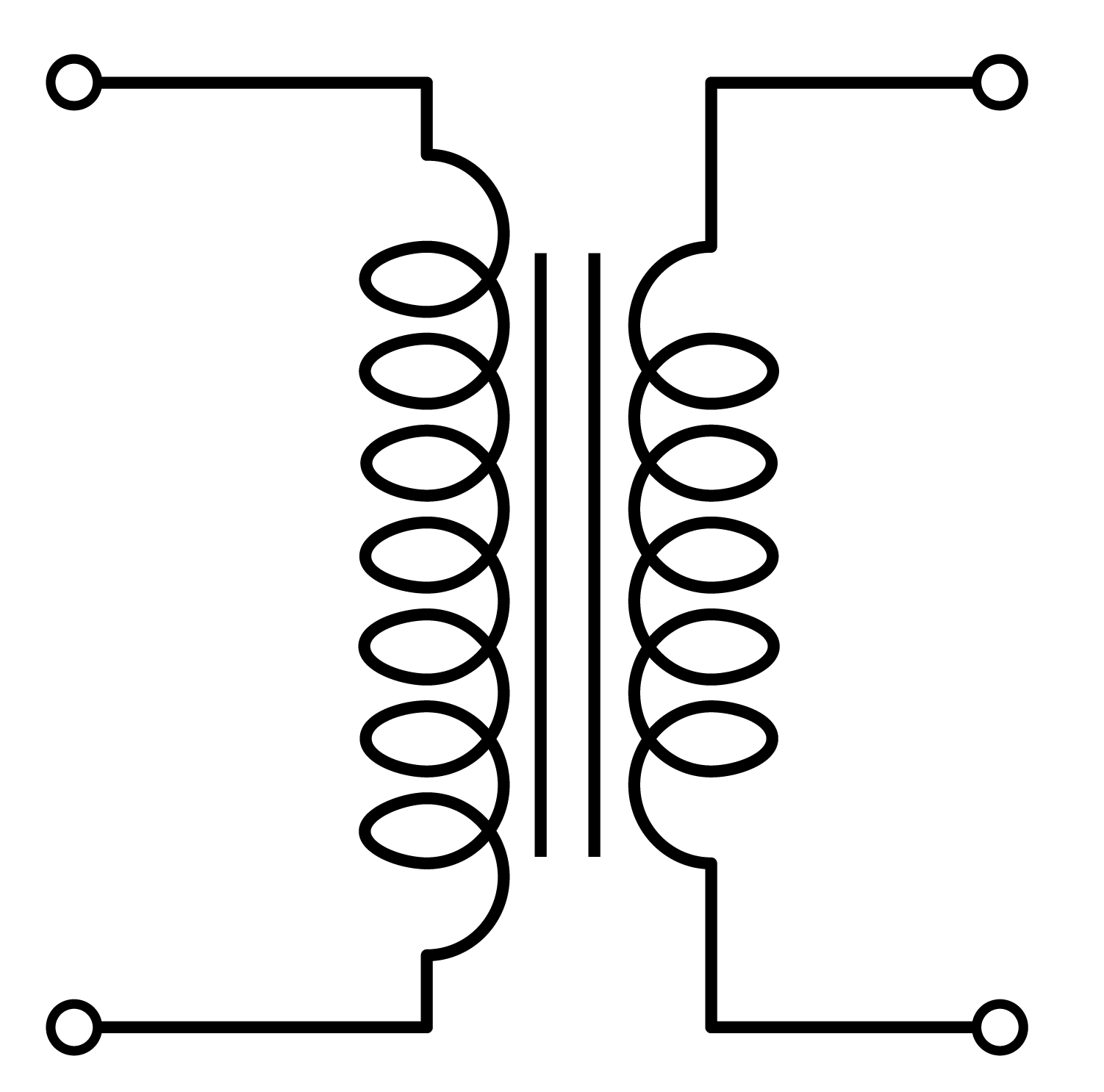
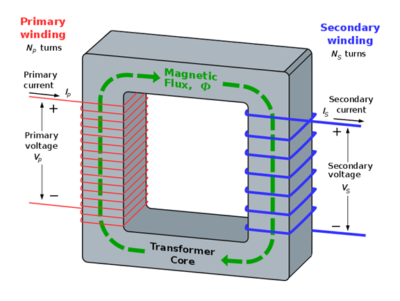
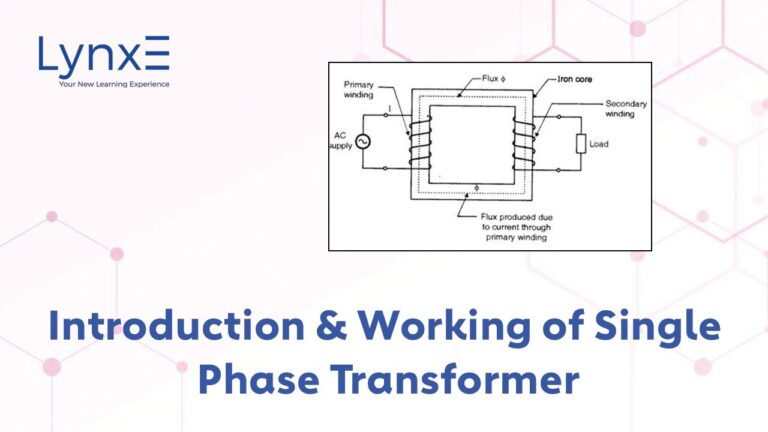
Step-down transformers consist of primary and secondary windings, usually made of copper, and a magnetic core. The primary winding receives the high voltage, while the secondary delivers the lower voltage. The core serves to enhance the transformer’s magnetic properties, facilitating efficient energy transfer without direct electrical connection between primary and secondary.
The Significance of Tangible Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of step-down transformers is critical for early detection of potential issues. Real-time data collection allows for the identification of anomalies that might be indicative of impending failures.
Real-Time Monitoring for Early Warnings
Real-time monitoring systems provide ongoing data about the transformer’s operating conditions. By tracking parameters such as temperature, voltage, and load, abnormalities can be detected early, preventing outages and equipment damage.
Identifying Problems Before They Escalate
Common transformer issues, including overheating, insulation degradation, and core damage, can be costly to repair and even more expensive if they lead to a power supply interruption. Early warning signs, such as unusual noise, voltage fluctuations, or oil leaks, signify the need for immediate attention.
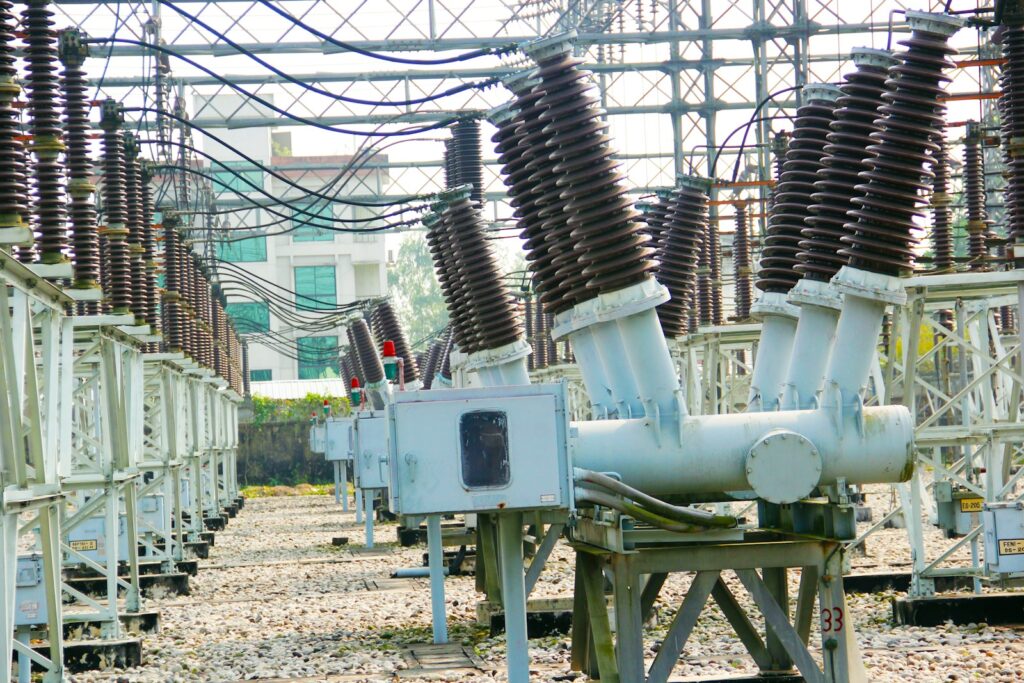

Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
The best defense is a strong offense. For transformers, that begins with a robust suite of diagnostic tools and techniques. These diagnostics are akin to medical examinations, allowing for a clear picture of the transformer’s health.
Overview of Diagnostic Tools
Several diagnostic tools are employed to assess a transformer’s state. These include Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) to detect developing faults, Frequency Response Analysis (FRA) to identify deformation in the transformer windings, and Partial Discharge testing to assess insulation integrity.
Detailed Diagnostic Tests
Dissolved Gas Analysis involves monitoring certain gases in the transformer oil, which are by-products of internal faults in the transformer. FRA, on the other hand, measures changes in winding properties, which can indicate movement of the internal structures. And Partial Discharge testing reveals the presence of insulation defects that can lead to eventual breakdowns.
Best Practices for Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance and monitoring are the cornerstones of an effective and resilient electrical system. Adhering to best practices ensures the longevity and reliability of step-down transformers.
Establishing Monitoring Schedules
Developing and following a strict monitoring schedule is imperative. This includes routine inspections, periodic tests, and continuous monitoring of important parameters. Establishing a baseline of normal operation can assist in more readily identifying deviations.
Impact of Proactive Monitoring
Proactive monitoring can result in significant costs savings by avoiding downtime and preventing secondary equipment damage that might occur in the event of a transformer failure. Case studies underscore the value of timely maintenance and the correlation between proactive approaches and system health.
The Future of Transformer Monitoring
The landscape of step-down transformer monitoring is not static. Emerging technologies promise to provide even greater insight and control over these vital assets. AI and IoT solutions are on the horizon, ready to revolutionize how transformers are monitored.
Emerging Technologies
Machine learning applications and IoT sensor networks offer the potential for highly predictive maintenance approaches. These technologies can understand current transformer conditions, predict future states, and recommend actions, creating a truly proactive maintenance regimen.
Transforming Diagnostic Capabilities
The use of advanced sensors and data analytics platforms can potentially enable transformers to report on their own health, akin to a biometric smart device synched with personalized health data. The diagnostic capability is on the cusp of becoming self-aware and incredibly insightful.
Conclusion: Committed to Continuous Improvement
The invisible world of electrical distribution is in the midst of a visible revolution. What was once reactive and reliant on crisis management is evolving into a proactive, continually improving system. Every step-down transformer that is diligently monitored and diagnostically attended, every hiccup that is preemptively rectified, is a testament to this enduring commitment.
It is not merely about electricity; it is about the communities and individuals that depend on it. It is about ensuring that the lights stay on, the equipment runs smoothly, and life as we know it continues unabated. The call-to-action is clear: integrate the best monitoring practices available, develop robust diagnostic methodologies, and stay at the vanguard of technological advancements. The stability and resiliency of our electrical infrastructure, after all, is not just a matter of power — it is a matter of vital continuity.