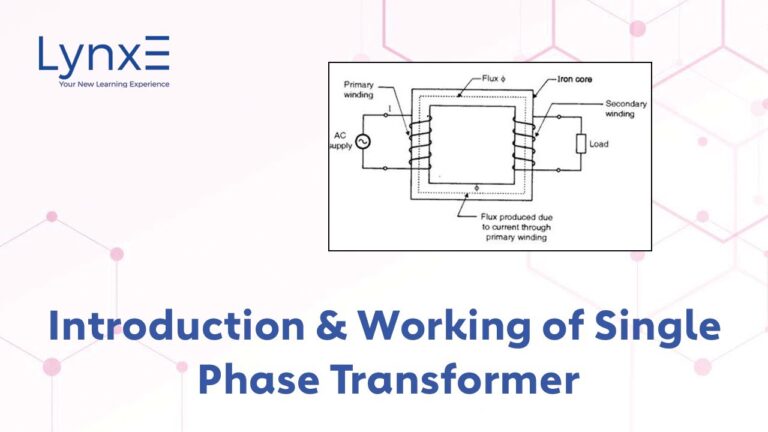
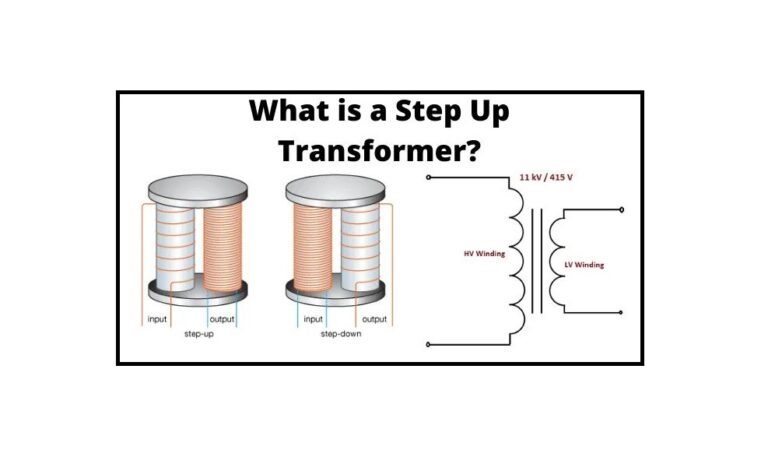
Industrial and Commercial Applications: Powering Industries with High Voltage Solutions
In the field of industrial engineering, power distribution is not just a technical matter but the very lifeblood of production. An efficient and stable power supply can significantly impact company performance, especially as industries continue to grow and evolve. High voltage solutions have emerged as the keystone in the arch of not only industrial revolution but also as the linchpin in modern commerce. This article will unpack the relevance and preeminence of high voltage solutions within the industrial and commercial realm, aiming to serve as an essential guide for engineers navigating this electrifying field.

Navigating Power Differentials: Low vs. High Voltage Systems
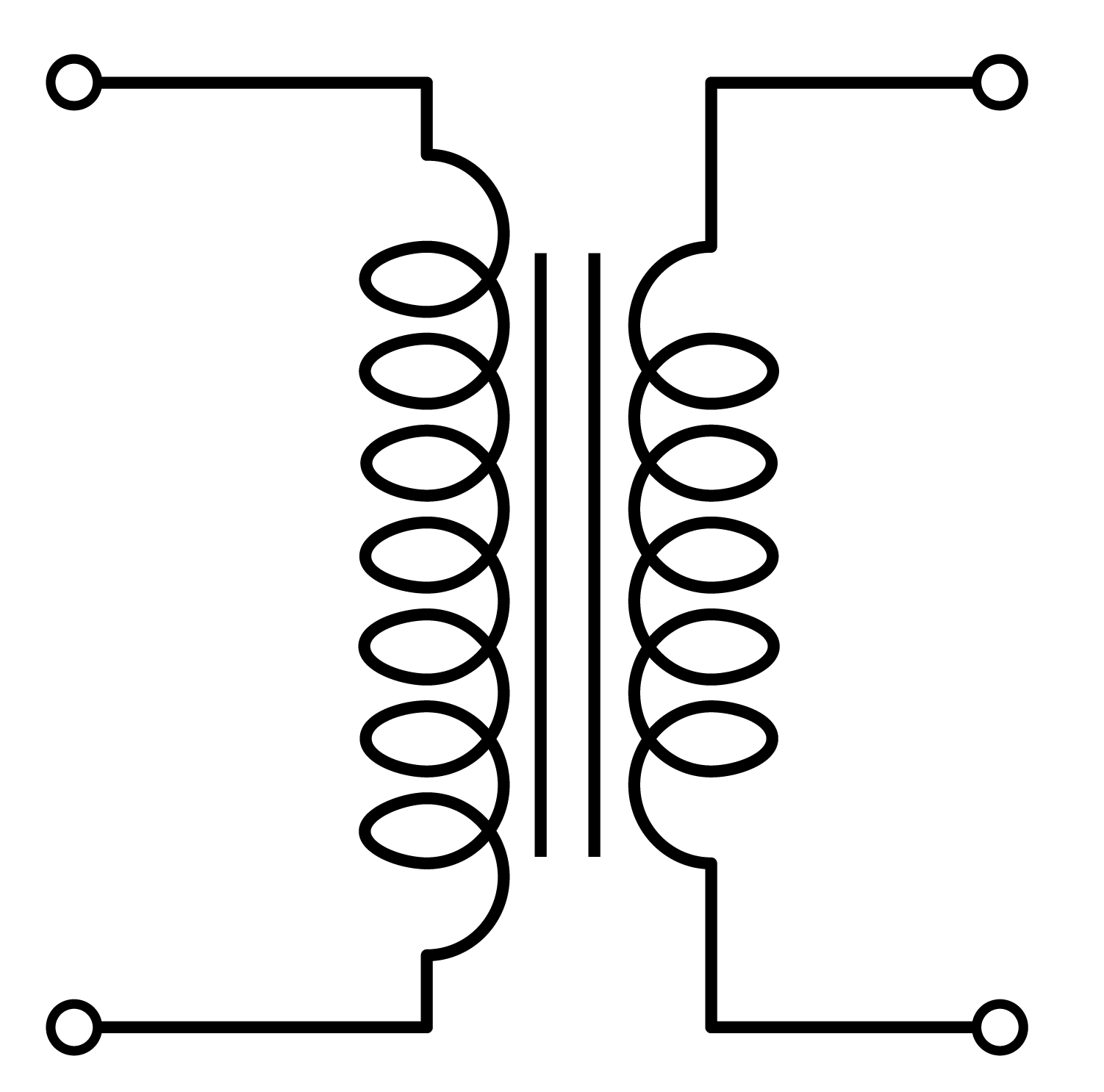
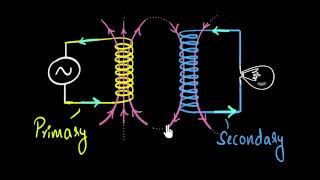
The first thing to understand about high voltage solutions is to delineate their regimes from low voltage systems. High voltage systems, operating at over 1000 volts, are integral in powering heavy industries with large-scale machinery and processes that demand substantial energy. Comparatively, low voltage systems are under 1000 volts and commonly found in smaller commercial settings and some light industrial applications. The distinction is not merely in numbers; it translates into the breadth of applications where high voltage reigns supreme.
Low Voltage Domains
Low voltage systems are the core of traditional electricity distribution networks, catering to daily consumer needs and small-scale commercial activities. These systems often rely on plug-and-play devices and are characterized by their user-friendly nature and ubiquity.
The Reach of High Voltage
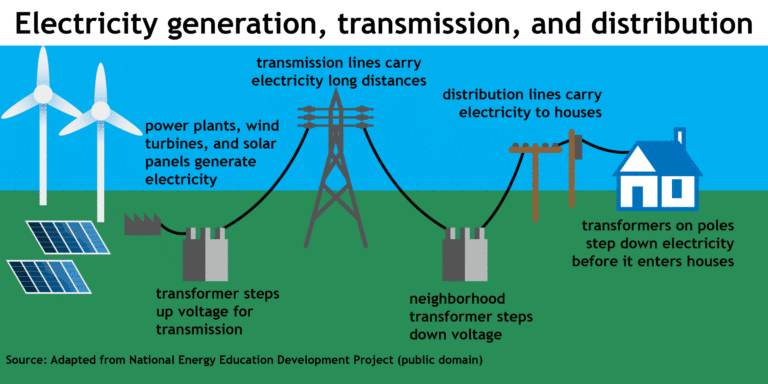
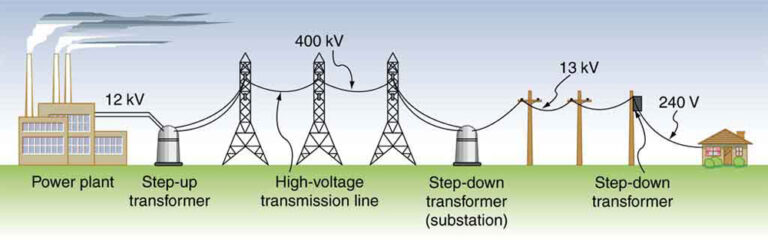
On the other end of the spectrum, high voltage systems form the backbone of mega-industries such as steel mills, chemical plants, and data centers, driving colossal motors, heating systems, and sophisticated processes. The capacity of high voltage systems to transmit power over significant distances, with minimized loss and to sustain energy-hungry operations, is the bedrock of modern industrial development.
Illuminating the Path to High Voltage Success
Understanding the difference between low and high voltage systems is just the first step. The real value lies in the practical examples where high voltage solutions have transformed industries, optimizing performance, and driving innovation forward.
Powering the Titans: Case Studies
Consider a steel manufacturing plant that upgraded its high voltage facilities. By doing so, it reduced energy wastage, improved the reliability of its operations, and saw considerable cost savings. Another shining example is a semiconductor foundry that harnessed high voltage technology to control its cleanroom environment with unprecedented precision, enhancing yield and quality of the products.
Unveiling the Gear Behind High Voltage Operations
To enable these successes, a sophisticated infrastructure is required. High voltage grid design involves meticulous planning to incorporate protection measures, such as circuit breakers and surge arresters, to ensure safety and limit equipment damage during faults. Engineers presiding over high voltage systems require a blend of foresight and precision to manage the potential hazards associated with high voltage operations, while at the same time, extracting the maximum out of this potent resource.
Safety: The Shock of High Voltage and Regulations
Safety within high voltage settings is non-negotiable. Engineers must adhere to stringent regulations and standards designed to protect workers, the public, and the environment.
Mission Control for Megawatts
The control room of a high voltage system is akin to the mission control of the power grid. This is where operators monitor and manage the flow of electricity, engage with high-tech visualizations of the network, and collaborate with emergency response teams in the event of a fault.
Compliant Currents
Adherence to regulations, like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards in the United States or similar entities globally, is a constant vigil for industrial engineers. Regular training, strict protocols, and advanced protective equipment are just some of the measures in place to ensure operations run safely and in compliance with the law.

The Grid of Tomorrow: Future-Proofing High Voltage Systems
With global shifts towards renewable energy sources and the burgeoning Internet of Things (IoT), the future of high voltage systems is set for dynamic changes that engineers must prepare for.
Renewable Electrification
The integration of renewable energy sources into high voltage operations is not without its complexities. Engineers must tackle challenges in energy storage, grid stability, and the integration of fluctuating power inputs from sources like wind and solar.
Smart Grids, Smarter Engineers
The era of smart grids, with their bidirectional flow of energy and enhanced communication capabilities, is approaching. The modern engineer, especially one in the high voltage domain, must be agile in learning and implementing new technologies that will redefine how power systems are monitored and managed.
Sparks of Conclusion
High voltage solutions are pivotal to the growth of heavy industries and the resilience of critical commercial operations. Engineers navigating this electrified terrain must be well-versed in the peculiarities of high voltage systems, with a keen eye toward innovation, safety, and the dynamic future of the industry. The electrification of industry is not just a trend but a mandate for sustainable growth and meaningful progress in the 21st century.
For any industrial engineer, mastering the art of the high voltage system is akin to wielding a powerful instrument. It demands respect, skill, and an ongoing dedication to learning and safety. As we forge ahead into uncharted territories of energy consumption and production, remember that while the road may be electrified, it is the hand of the adept engineer that steers the wheel.